Some living systems instead use an inorganic molecule other than O 2 , such as sulfate, as a final electron acceptor for an electron transport chain. This process, called anaerobic cellular respiration, is performed by some bacteria and archaea.
Unraveling Cellular Respiration: A Comprehensive Guide – SS Publishers & Distributors
The electron transport chain is a series of electron transporters embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane that shuttles electrons from NADH and FADH 2 to molecular oxygen. In the process, protons are pumped from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space, and oxygen is reduced to form water. The electron transport chain (Figure 1

Source Image: ozmo.io
Download Image
The electron on the lowest step also has an arrow pointing towards an electron at the base of the steps, and next to that electron is a chemical formula that says electron plus oxygen plus 2 hydrogen ions produces water. … Cellular respiration is an absolutely essential process for any cell because it’s how it produces energy. Cells need
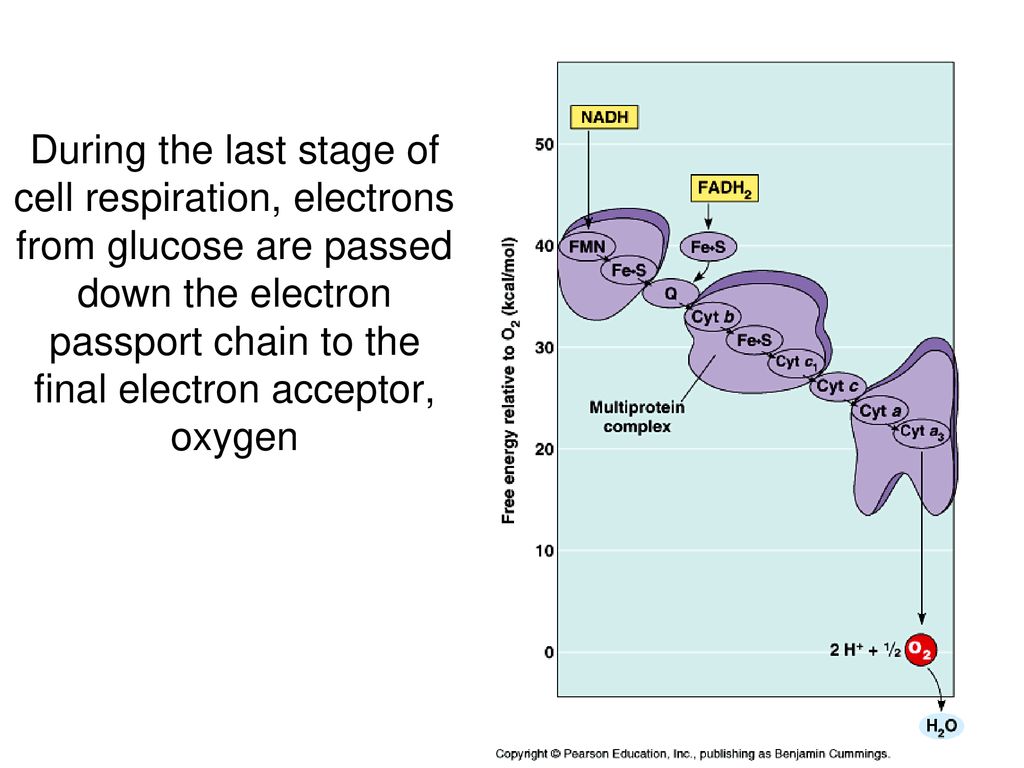
Source Image: slideplayer.com
Download Image
Best Electron Transport Chain Royalty-Free Images, Stock Photos & Pictures | Shutterstock
We call this process respiration, specifically aerobic respiration. We breath in oxygen, it diffuses into our cells and to our mitochondria where it is used as the final acceptor of electrons from our electron transport chains. That is aerobic respiration: the process of using oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor in an electron transport chain.
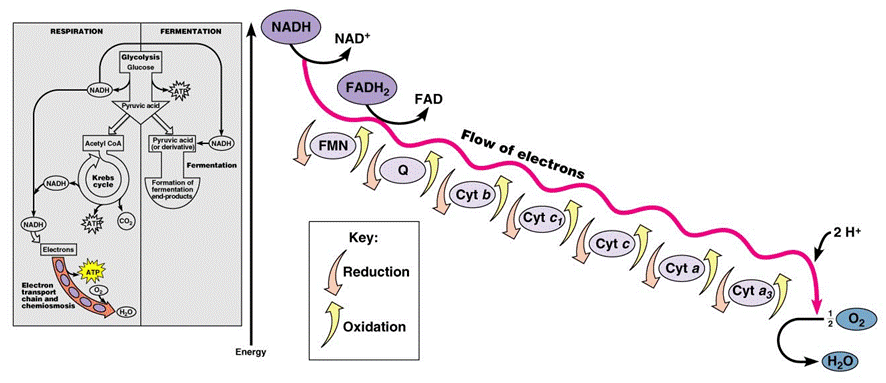
Source Image: mrgscience.com
Download Image
What Is The Final Electron Acceptor In Cellular Respiration
We call this process respiration, specifically aerobic respiration. We breath in oxygen, it diffuses into our cells and to our mitochondria where it is used as the final acceptor of electrons from our electron transport chains. That is aerobic respiration: the process of using oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor in an electron transport chain.
At the end of the electron transport chain, the final electron acceptor, O 2, combines with protons to produce water (H 2 O). Meanwhile, ATP synthase uses the movement of protons back into the mitochondrial matrix for ATP synthesis. Where does cellular respiration take place?
Topic 8.2 Cell Respiration – AMAZING WORLD OF SCIENCE WITH MR. GREEN
The electron transport chain is the portion of aerobic respiration that uses free oxygen as the final electron acceptor of the electrons removed from the intermediate compounds in glucose catabolism. The electron transport chain is composed of four large, multiprotein complexes embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane and two small
8.3 Cellular Respiration – Microbiology: Canadian Edition
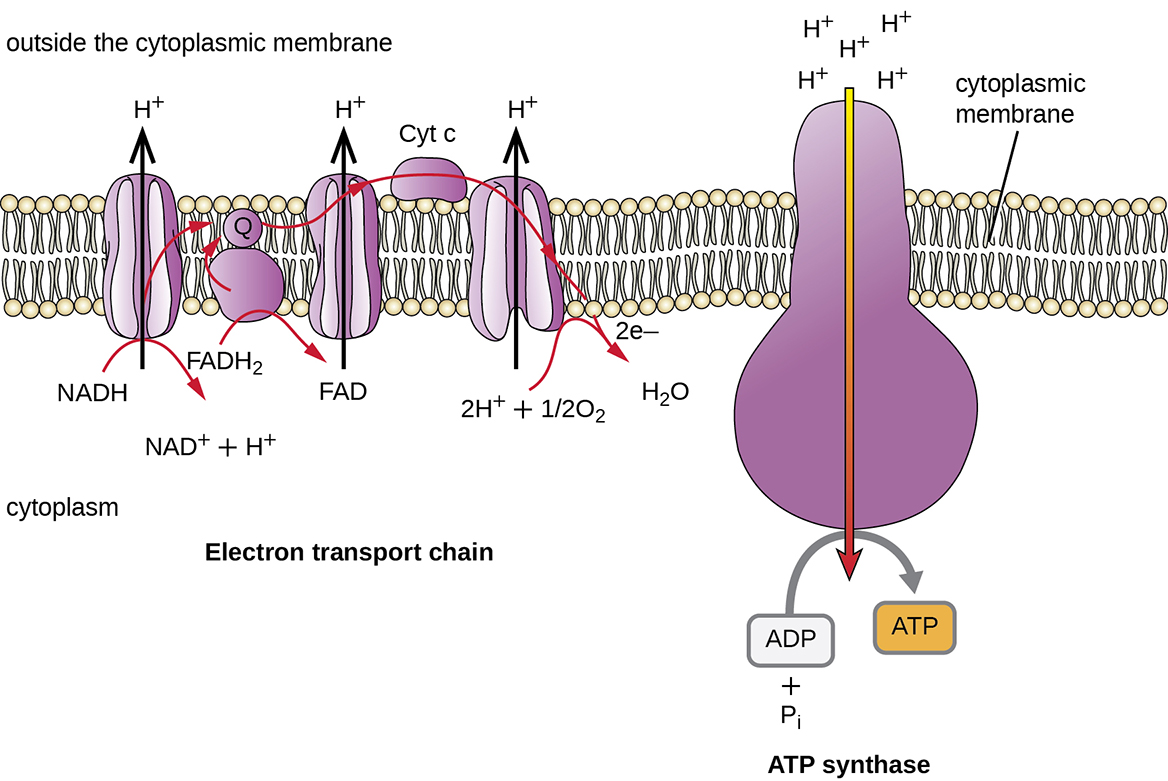
Source Image: ecampusontario.pressbooks.pub
Download Image
Principles of Biochemistry Chapter 14 – team.no.sleep
The electron transport chain is the portion of aerobic respiration that uses free oxygen as the final electron acceptor of the electrons removed from the intermediate compounds in glucose catabolism. The electron transport chain is composed of four large, multiprotein complexes embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane and two small

Source Image: teamnosleepweb.wordpress.com
Download Image
Unraveling Cellular Respiration: A Comprehensive Guide – SS Publishers & Distributors
Some living systems instead use an inorganic molecule other than O 2 , such as sulfate, as a final electron acceptor for an electron transport chain. This process, called anaerobic cellular respiration, is performed by some bacteria and archaea.

Source Image: ssjpd.com
Download Image
Best Electron Transport Chain Royalty-Free Images, Stock Photos & Pictures | Shutterstock
The electron on the lowest step also has an arrow pointing towards an electron at the base of the steps, and next to that electron is a chemical formula that says electron plus oxygen plus 2 hydrogen ions produces water. … Cellular respiration is an absolutely essential process for any cell because it’s how it produces energy. Cells need

Source Image: shutterstock.com
Download Image
What is fermentation in cellular respiration? – Quora
In cellular respiration, oxygen is the final electron acceptor. Oxygen accepts the electrons after they have passed through the electron transport chain and ATPase, the enzyme responsible for creating high-energy ATP molecules. Just remember cellular respiration—respiration means breathing, and you cannot breathe without oxygen.
Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
Respiration In Plants Notes – WBBSE Solutions
We call this process respiration, specifically aerobic respiration. We breath in oxygen, it diffuses into our cells and to our mitochondria where it is used as the final acceptor of electrons from our electron transport chains. That is aerobic respiration: the process of using oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor in an electron transport chain.

Source Image: wbbsesolutions.guide
Download Image
SOLUTION: The process of photosynthesis – Studypool
At the end of the electron transport chain, the final electron acceptor, O 2, combines with protons to produce water (H 2 O). Meanwhile, ATP synthase uses the movement of protons back into the mitochondrial matrix for ATP synthesis. Where does cellular respiration take place?

Source Image: studypool.com
Download Image
Principles of Biochemistry Chapter 14 – team.no.sleep
SOLUTION: The process of photosynthesis – Studypool
The electron transport chain is a series of electron transporters embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane that shuttles electrons from NADH and FADH 2 to molecular oxygen. In the process, protons are pumped from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space, and oxygen is reduced to form water. The electron transport chain (Figure 1
Best Electron Transport Chain Royalty-Free Images, Stock Photos & Pictures | Shutterstock Respiration In Plants Notes – WBBSE Solutions
In cellular respiration, oxygen is the final electron acceptor. Oxygen accepts the electrons after they have passed through the electron transport chain and ATPase, the enzyme responsible for creating high-energy ATP molecules. Just remember cellular respiration—respiration means breathing, and you cannot breathe without oxygen.